
Unfortunately, there’s some outdated and false information you can find on the web about the toxicity of hobo and wolf spiders to pets. But they’re more commonly found indoors than black widows. Like black widows, brown recluses aren’t aggressive and like to live in dark, undisturbed areas outside and indoors. They are various shades of brown, have a violin-shaped marking on their upper abdomen, and have fine hairs covering their bodies and legs. Males are usually smaller than females, but both males and females are toxic. The adult brown recluse spider’s body is about 3-8 millimeters long with a leg span of around 24 millimeters. Brown Recluseīrown recluse spiders, also known as fiddleback or violin spiders, mainly live in the central Midwestern states and southward from Texas to western Georgia. Found in both urban and rural areas, black widows prefer to live in warm, dark, secluded places and are not aggressive. Males are about half the size of females, can be black or brown, and lack the hourglass marking. Only the females are toxic. They’re shiny and black with a red or orange hourglass-shaped marking on the underside of their abdomen. Adult female black widows are about 38 millimeters long with their leg span and a 12-16 millimeter-long body. but are more common in the South and West.

Black Widowīlack widow spiders live throughout the U.S. The venom delivered by a bite from these spiders can cause serious effects, which may require immediate veterinary attention. Far less common are red and brown widow spiders.

for pets (and humans) are the black widow ( Latrodectus species) and brown recluse ( Loxosceles species). The most common dangerous spiders in the U.S. Unfortunately, there are exceptions all spiders are dangerous.
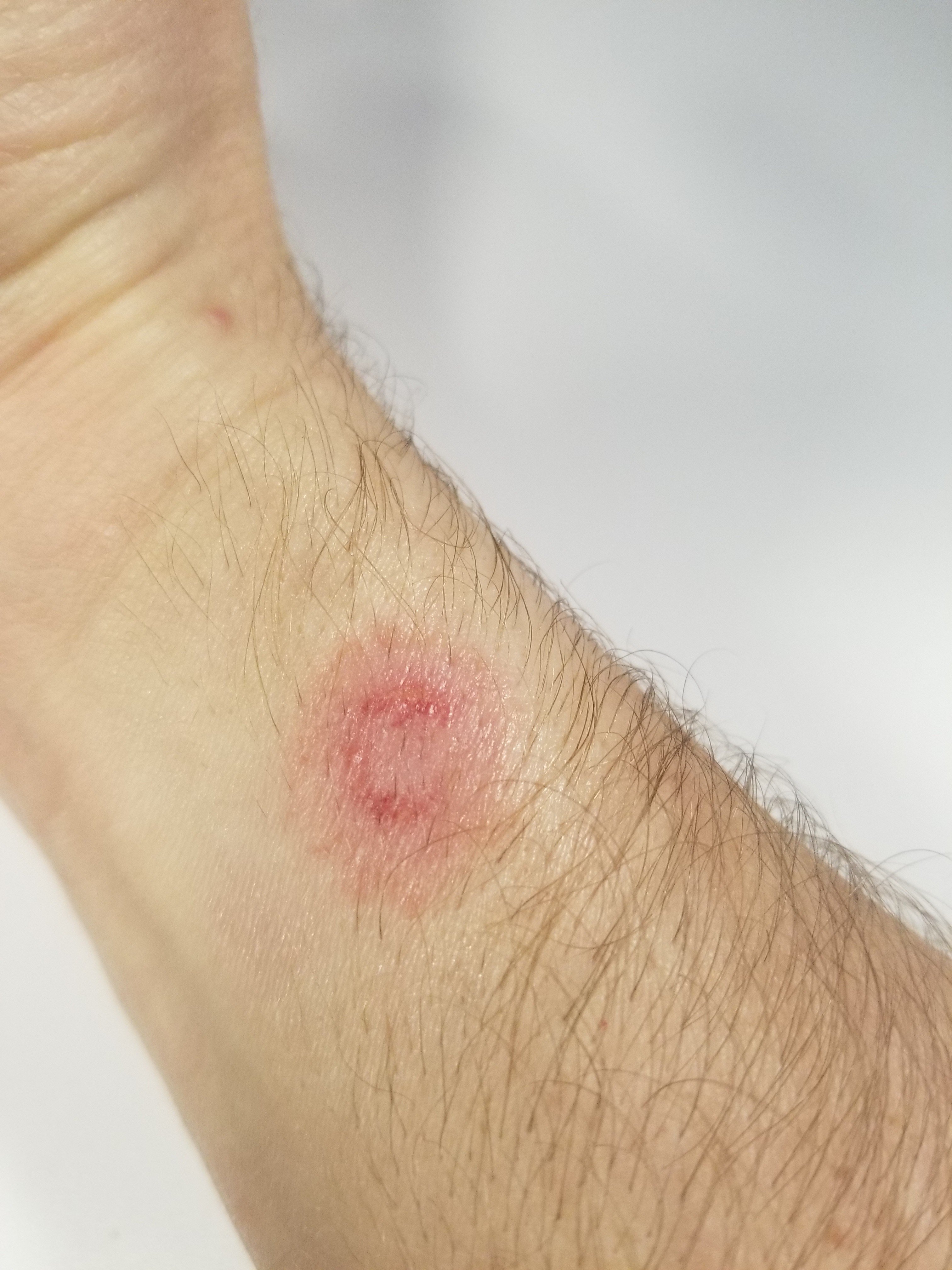
How Can Pet Insurance Help With Emergencies?. 13, 14 These patterns resemble a violin, fiddle, or cello (with the base at the head end), bordered by three pairs of eyes 13 – 15 ( Figure 2B). 13, 14 Female recluses are more venomous and generally larger than males (leg spans of 20 to 30 mm compared with 10 to 35 mm), and they have distinctive, darker brown patterns on the dorsal cephalothorax. All Loxosceles spiders are brown, often have no unique identifying markings (except for female brown recluse spiders ), and often are simply described as brown spiders. 7 All Loxosceles spiders in the United States may cause bites characterized by necrotic arachnidism with dermonecrotic ulceration at bite sites, presumably because of autoimmune responses from cytokines and lymphocytes and cytotoxicity from venom components (mainly sphingomyelinase D). Loxosceles spiders are most abundant and active at night during the warmer months. The six species of recluse spiders in the United States include Loxosceles arizonica, Loxosceles deserta, Loxosceles devia, Loxosceles laeta, Loxosceles rufescens, and Loxosceles reclusa ( Figure 2). One study found no deaths in 111 patients with entomologist-confirmed Loxosceles reclusa bites. Most necrotizing ulcers will heal over one to eight weeks with a 10 to 15 percent incidence of major scarring. Resolution of all manifestations over two or three days death rarely occurs Potential associated signs of systemic toxicityĪrthralgias, bronchorrhea, regional or generalized diaphoresis, fever, hypertension, hyperreflexia, regional lymphadenopathy, nausea, vomiting, paresthesias, priapism, ptosis, restlessness, salivationįebrile seizures, hemoglobinuria, myoglobinuria, acute renal failure Muscular spasm and rigidity beginning at bite site and spreading proximally to abdomen and face rebound tenderness mimicking acute appendicitis is possible.Īrthralgias, fever, chills, maculopapular rash, nausea, vomiting Incubation period from bite to systemic toxicity Present usually atypical and rarely full-blown (latrodectism) Local cytotoxicity with subsequent ulcerating dermonecrosis Massive presynaptic discharge of all autonomic neurotransmitters Painless or minimally painful localized inflammation that subsequently spreads Moderately to severely painful little or no surrounding inflammation







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
